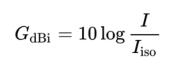Knowledge
RF Coaxial Cable Part numbers and Parameters
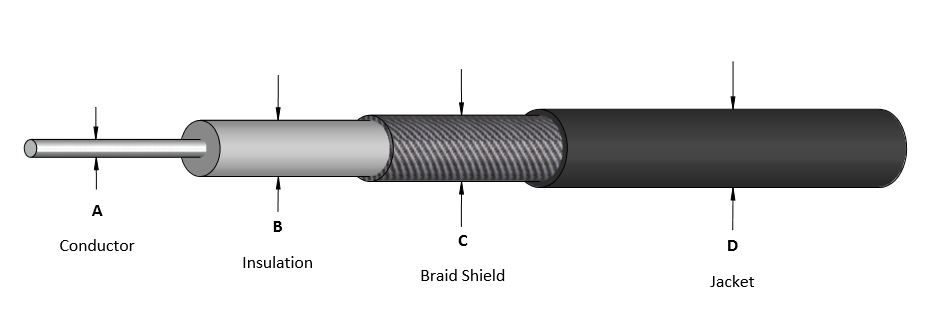
Coaxial cable, Self-shielded cable used for transmission of communications signals, such as those for television, telephone, or computer networks. A coaxial cable consists of two conductors laid concentrically along the same axis. One conducting wire is surrounded by a dielectric insulator, which is in turn surrounded by the other, outer conductor, producing an electrically shielded transmission circuit. The whole cable …
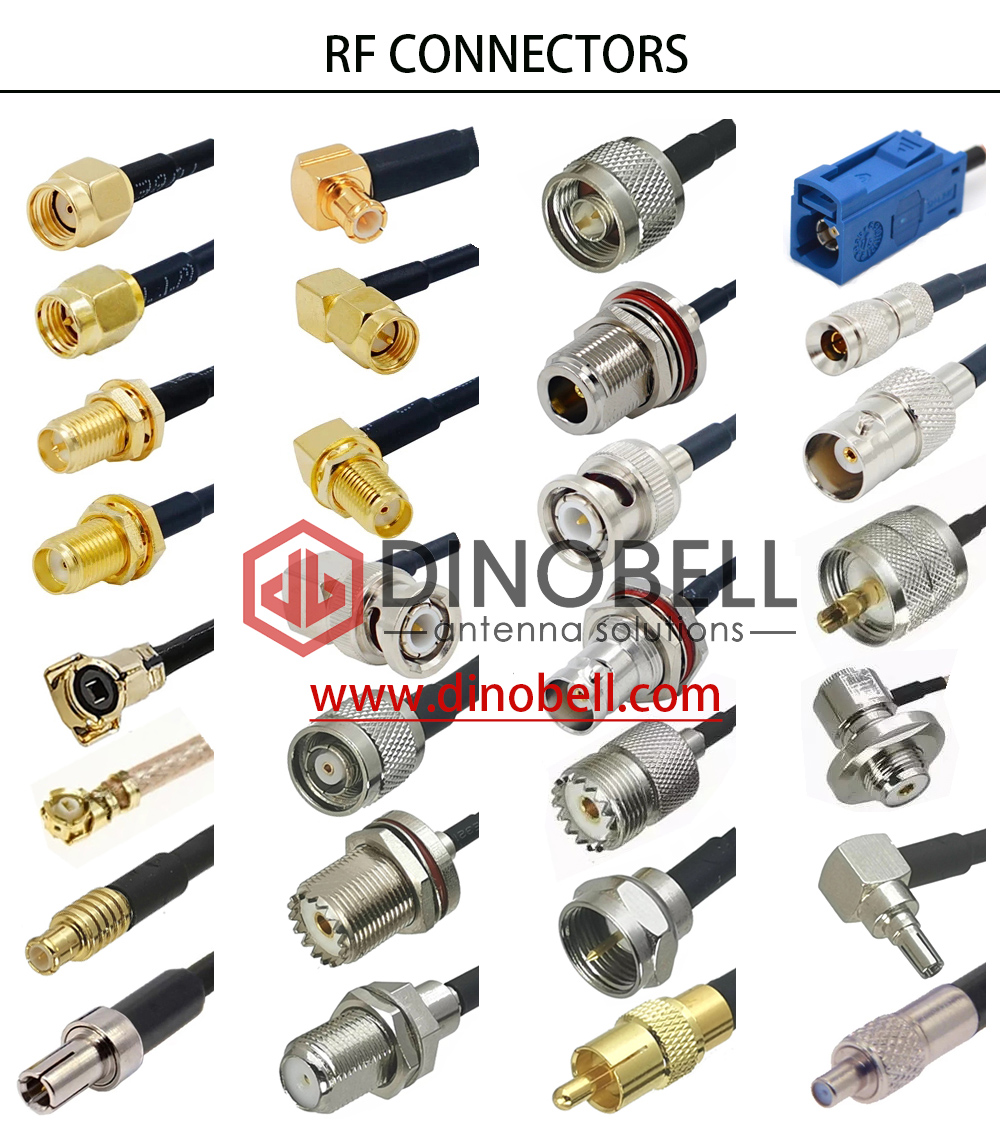
RF Coaxial Connector Frequency Ranges
All RF coaxial connector types were designed with a specific purpose in mind. Certain applications require acceptable performance across a range of frequencies in conditions ranging from controlled laboratory settings (metrology, production test) to extremely harsh outdoor environments that need protection from wind, rain, ice, and extreme temperatures. In many instance, physical size is an issue both for space considerations …
5G Introduction and FAQs
What is 5G? 5G is the 5th generation mobile network. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. 5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices. 5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra low …
LoRawan Frequency Plans by Country
LoRawan Frequency Plans by Country This document is only a summary of radio regulations, and the appropriate frequency plans that should be used for the respective countries, for reference only. A Country Frequency Plan Regulatory document Afghanistan Albania EU863-870 EU433 CEPT Rec. 70-03 Algeria CONDITIONS D’UTILISATION DES EQUIPEMENTS D’IDENTIFICATION PAR RADIOFREQUENCES – RFID Andorra EU863-870 EU433 CEPT Rec. 70-03 Angola …
Mounting Types Choose
In order to select the most optimized antenna, start by confirming if the antenna will be integrated internally, such as a mobile device or externally which often comes with housing for protection in outdoor application and installation. Dinobell offers a large selection for internal and external single and combination antenna mounting types. A. For External Single and Combination Antennas …
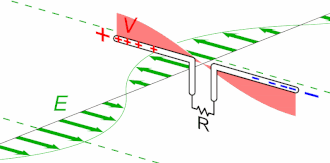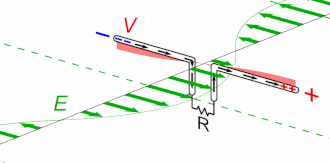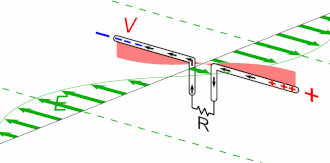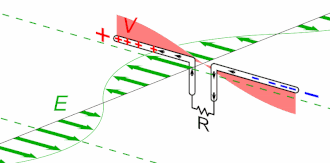
Effect of Ground
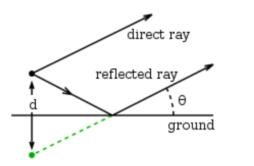
Effect of Ground Ground reflections is one of the common types of multipath. The radiation pattern and even the driving point impedance of an antenna can be influenced by the dielectric constant and especially conductivity of nearby objects. For a terrestrial antenna, the ground is usually one such object of importance. The antenna’s height above the ground, as well …
Antenna Parameters Explanation
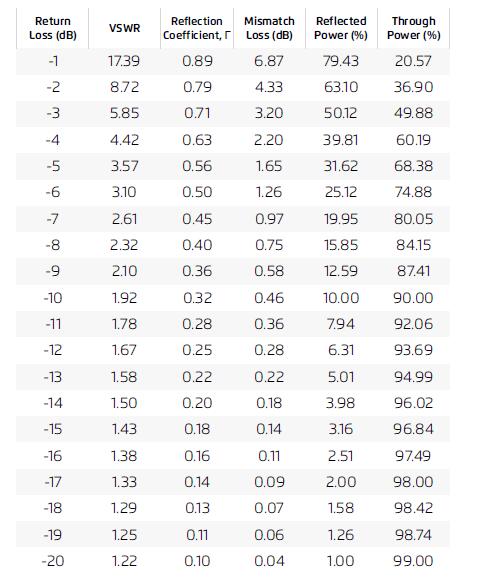
1. Return Loss The return loss is measured in decibels (dB) and represents how much energy is transferred from the device to the antenna. The lower the measurement the better. For a 50 Ohm system, it is recommended to have a minimum of -5dB or better measurement. Using the return loss to identify how the impedance of the antenna performs …
Electrically short antennas
It is possible to use simple impedance matching techniques to allow the use of monopole or dipole antennas substantially shorter than the 1⁄4 or 1⁄2 wavelength, respectively, at which they are resonant. As these antennas are made shorter (for a given frequency) their impedance becomes dominated by a series capacitive (negative) reactance; by adding an appropriate size “loading coil” – …
Antenna Types – Traveling wave Antenna
Antenna Types – Traveling wave Antenna Animation showing a Beverage antenna . Quadrant antenna, similar to rhombic, at an Austrian shortwave broadcast station. Radiates horizontal beam at 5-9 MHz, 100 kW Array of four axial-mode helical antennas used for satellite tracking, France Unlike the above antennas, traveling wave antennas are not resonant so they have inherently broad bandwidth. They are …
Antenna Types – Monopole Antenna
Monopole Antenna Quarter-wave whip antenna on an FM radio for 88-108 MHz Rubber Ducky antenna on UHF 446 MHz walkie talkie with rubber cover removed. VHF ground plane antenna T antenna of amateur radio station, 80 ft high, used at 1.5 MHz. Mast radiator antenna of medium wave AM radio station, Germany Folded unipole with skirt wires connected at a …
Antenna Types – Loop Antenna
Antenna Types – Loop Antenna Ferrite loopstick antenna from an AM broadcast radio, about 4 in (10 cm) long. The antenna is inductive and, in conjunction with a variable capacitor, forms the tuned circuit at the input stage of the receiver. Loop antenna for transmitting at high frequencies, 2m diameter Separate loop antenna for AM radio A two-element quad antenna …
Antenna Types – Isotropic Antenna
An isotropic antenna (isotropic radiator) is a hypothetical antenna that radiates equal signal power in all directions, often compared to an incandescent lightbulb. It is a mathematical model that is used as the base of comparison to calculate the directionality or gain of real antennas. No real antenna can have an isotropic radiation pattern, but the isotropic radiation pattern serves …
Antenna Types – Dipole Antenna
Dipole Antenna Rabbit ears” dipole variant for VHF television reception Two-element turnstile antenna for reception of weather satellite data, 137 MHz. Has circular polarization. Corner reflector UHF TV antenna with “bowtie” dipole driven element at its center The dipole is the prototypical antenna on which a large class of antennas are based. A basic dipole antenna consists of two …
Antenna Types – Conical Antenna
Biconical antenna is a dipole-like antenna made of two cones, oriented along the same axis and oriented tip-to-tip. Butterfly antenna is a two-dimesional (flat) biconical antenna. A butterfly antenna discone antenna is half of a biconical with a flat disc mounted above the cone Discone antenna dimensions
Arrays and reflectors
The amount of signal received from a distant transmission source is essentially geometric in nature due to the inverse-square law, and this leads to the concept of effective area. This measures the performance of an antenna by comparing the amount of power it generates to the amount of power in the original signal, measured in terms of the signal’s power …
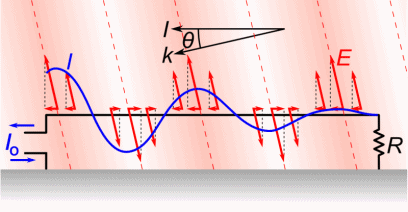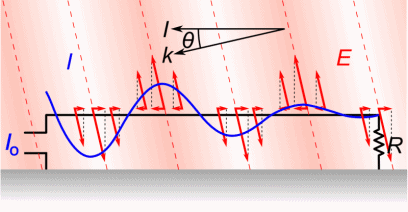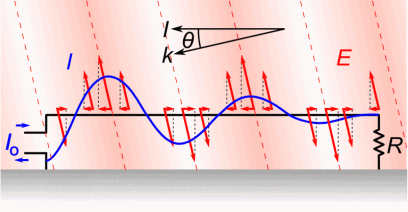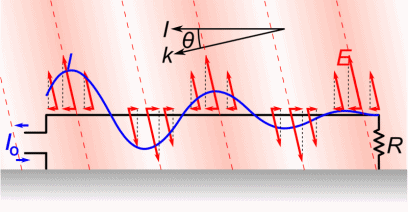
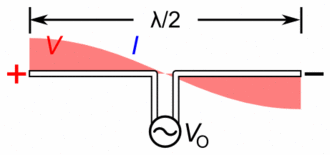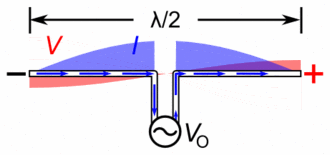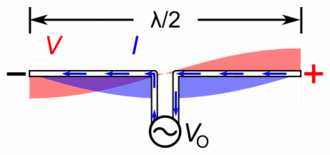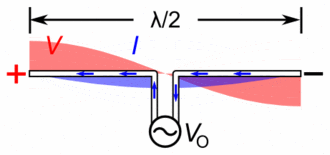
Antenna Current and Voltage Distribution
The quarter-wave elements imitate a series-resonant electrical element due to the standing wave present along the conductor. At the resonant frequency, the standing wave has a current peak and voltage node (minimum) at the feed. In electrical terms, this means the element has minimum reactance, generating the maximum current for minimum voltage. This is the ideal situation, because it produces …
Antenna Types – Array Antenna
Antenna Types – Array Antenna VHF collinear array of folded dipoles Yagi-Uda television antenna for analog channels 2-4, 47-68 MHz Log-periodic dipole array covering 140-470 MHz Sector antennas (white bars) on cell phone tower. Collinear arrays of dipoles, these radiate a flat, fan-shaped beam. Reflective array UHF TV antenna, with bowtie dipoles to cover the UHF 470-890 MHz band …
Antenna Types – Aperture Antenna
Antenna Types – Aperture Antenna NASA Cassegrain parabolic spacecraft communication antenna, Australia. Uses X band, 8 – 12 GHz. Extremely high gain ~70 dBi. Microwave horn antenna bandwidth 0.8–18 GHz X band marine radar slot antenna on ship, 8 – 12 GHz. Dielectric lens antenna used in millimeter wave radio telescope Aperture antennas are the main type of directional antennas …
Different Antenna Types
In radio systems, many different antenna types are used with specialized properties for particular applications. Antennas can be classified in various ways. The list below groups together antennas under common operating principles, following the way antennas are classified in many engineering textbooks. The dipole, monopole, array and large loop antenna types below typically function as resonant antennas; waves of …
Key Characteristics of Antenna
Key Characteristics of Antenna It is a fundamental property of antennas that the electrical characteristics of an antenna , such as gain, radiation pattern, impedance, bandwidth, resonant frequency and polarization, are the same whether the antenna is transmitting or receiving. For example, the “receiving pattern” (sensitivity as a function of direction) of an antenna when used for reception is identical …
Antenna Resonance
The majority of antenna designs are based on the resonance principle. This relies on the behaviour of moving electrons, which reflect off surfaces where the dielectric constant changes, in a fashion similar to the way light reflects when optical properties change. In these designs, the reflective surface is created by the end of a conductor, normally a thin metal wire …
Antenna Overview
Antennas are required by any radio receiver or transmitter to couple its electrical connection to the electromagnetic field.Radio waves are electromagnetic waves which carry signals through the air (or through space) at the speed of light with almost no transmission loss. Antennas can be classified as omnidirectional, radiating energy approximately equally in all directions, or directional, where energy radiates …
Terminology of Antenna and Aerial
Terminology of Antenna and Aerial Electronic symbol for an antenna The word “ antenna” comes from a part of latin military ship. The words antenna and aerial are used interchangeably. Occasionally the equivalent term “aerial” is used to specifically mean an elevated wire antenna. The origin of the word antenna relative to wireless apparatus is attributed to Italian radio pioneer …
Introduce of Antenna and Aerial
Introduce of Antenna and Aerial In radio engineering, an antenna is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver.In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna’s terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In reception, …